
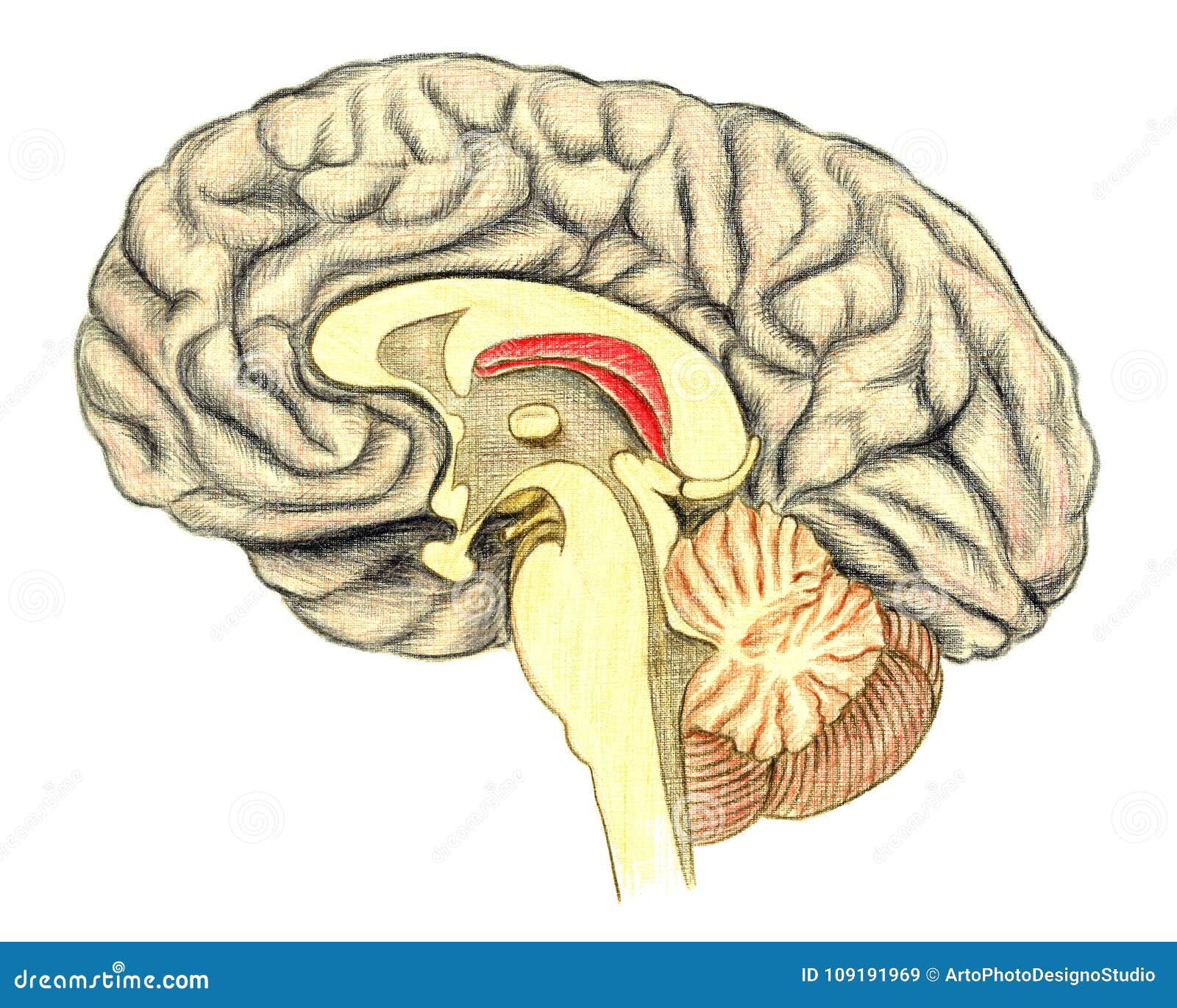
Yet white matter makes up half the human brain and has not been thought to be important in cognition or learning outside the context of pathology. “Gray matter” is only one of two types of brain tissue the other “white matter” is rarely mentioned. Is it normal to have white matter in the brain? Neuroscientists at a UC Berkeley lab have uncovered evidence that a well-known stress hormone trips a switch in stem cells in the brain, causing them to produce a white matter cell that ultimately can change the way circuits are connected in the brain. Many of these nerve fibers are surrounded by a type of sheath or covering called myelin. It contains nerve fibers (axons), which are extensions of nerve cells (neurons). White matter is found in the deeper tissues of the brain (subcortical). What parts of the brain are white matter? White matter is made of axons connecting different parts of grey matter to each other. The CNS has two kinds of tissue: grey matter and white matter, Grey matter, which has a pinkish- grey color in the living brain, contains the cell bodies, dendrites and axon terminals of neurons, so it is where all synapses are.

There may be increased amounts of water between the myelinated fibers, etc. It may be that scar tissue is formed within the white matter. It may be that innumerable vacuoles are formed within the myelin sheath.

It may be that the myelin was formed all right, but is now broken down and lost. It may be that there is a lack of myelin because the myelin was never made in sufficient amounts. White matter abnormalities on MRI can have different bases on tissue level. The diagnosis is usually made on the basis of MRI findings. These are called "the white matter disorders". In many neurological disorders in childhood, the white matter of the brain is predominantly involved. Consequently, brain functions become hampered or be lost. When the myelin sheath is damaged or disappears, the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers slows down or fails completely. Myelin is an essential part of the white matter. Through its special construction, myelin accelerates the propagation of impulses along nerve fibers. Insulation is important for the prevention of short-circuits. The myelin sheath has two functions: insulation and acceleration of impulse conduction. Myelin is a fatty sheath wrapped around nerve fibers. The nerve fibers form the connections between the nerve cells. The white matter of the brain is composed of nerve fibers and myelin. The gray matter contains the nerve cells. The brain of humans consists of gray matter and white matter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
